In the realm of physics, the cart on ramp physics lab stands as a captivating exploration into the fundamental principles of motion and energy. As a cart embarks on its journey down an inclined plane, it becomes a living testament to the interplay of these concepts, offering a hands-on learning experience that sparks curiosity and ignites a passion for scientific inquiry.
This immersive lab delves into the theoretical foundations of motion, introducing concepts such as velocity, acceleration, and energy conservation. Through meticulous data collection and analysis, students uncover the intricate relationships between these parameters, gaining a deeper understanding of the physical world around them.
Introduction to Cart on Ramp Physics Lab

The Cart on Ramp Physics Lab is an introductory experiment designed to investigate the principles of motion and energy. It involves rolling a cart down a ramp and measuring its velocity, acceleration, and energy at different points along the ramp.
The lab provides hands-on experience with:
- Measuring motion using motion sensors
- Calculating velocity, acceleration, and energy
li>Applying the laws of motion and energy to real-world situations
Background Information on Motion and Energy
Motion is the change in position of an object over time. Velocity is the rate of change of position, and acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. Energy is the ability to do work, and it can exist in different forms, such as kinetic energy (energy of motion) and potential energy (energy due to position).
The laws of motion and energy describe how objects move and interact. Newton’s laws of motion explain how forces affect the motion of objects, while the law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed.
Materials and Equipment
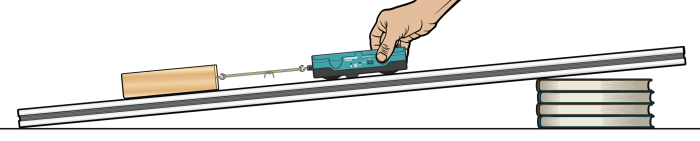
The Cart on Ramp Physics Lab requires a range of materials and equipment to conduct experiments and collect data.
These include:
Cart
- A cart is a small, wheeled vehicle used to transport objects or materials.
- In this lab, the cart will be used to carry weights and move down the ramp.
Ramp
- A ramp is an inclined plane that allows objects to move from one level to another.
- The ramp in this lab will be used to create an inclined plane for the cart to roll down.
Weights
- Weights are objects with a known mass that can be added to or removed from the cart.
- In this lab, weights will be used to change the mass of the cart and observe how it affects its motion.
Meter Stick
- A meter stick is a measuring device used to measure distances.
- In this lab, the meter stick will be used to measure the length of the ramp and the distance traveled by the cart.
Stopwatch
- A stopwatch is a timing device used to measure the time it takes for an event to occur.
- In this lab, the stopwatch will be used to measure the time it takes for the cart to travel down the ramp.
Data Table
- A data table is a spreadsheet used to organize and record experimental data.
- In this lab, the data table will be used to record the mass of the cart, the length of the ramp, the distance traveled by the cart, and the time it takes for the cart to travel down the ramp.
Experimental Setup
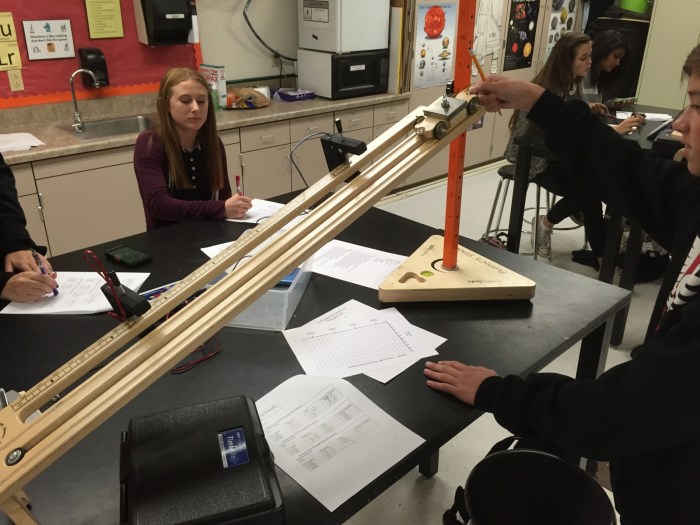

Setting up the experiment is crucial for accurate data collection. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Ramp Placement
- Securely clamp the ramp on a stable surface, ensuring it is level.
- Adjust the height of the ramp to the desired angle of inclination.
Cart Preparation
- Place the cart at the starting point on the ramp.
- Check if the cart is free from any obstacles or friction.
Measuring Devices, Cart on ramp physics lab
- Position a motion sensor at the bottom of the ramp to measure the cart’s velocity.
- Place a ruler or tape measure along the ramp to measure the distance traveled by the cart.
Data Collection and Analysis: Cart On Ramp Physics Lab

To accurately measure the cart’s motion, we employ various techniques for data collection. These methods capture crucial information that allows us to determine the cart’s velocity, acceleration, and other relevant parameters.
One essential aspect of data collection involves measuring the cart’s displacement along the ramp. This can be achieved using a motion sensor or a simple ruler. The sensor or ruler provides a continuous record of the cart’s position over time, enabling us to calculate its displacement.
In addition to displacement, we also measure the time it takes for the cart to travel along the ramp. A stopwatch or a data acquisition system can be used for this purpose. By accurately measuring the time interval, we can determine the cart’s average velocity and acceleration.
Once the displacement and time data have been collected, we can analyze them to extract meaningful information about the cart’s motion. One common method of analysis is to plot a graph of displacement versus time. This graph provides a visual representation of the cart’s motion and allows us to determine its velocity and acceleration from the slope and curvature of the graph, respectively.
Another method of analysis involves using mathematical equations to calculate the cart’s velocity and acceleration. These equations, derived from the laws of motion, allow us to determine the cart’s motion based on its displacement and time data.
The cart on ramp physics lab is a great way to learn about the laws of motion. You can use a variety of different carts and ramps to experiment with how different factors affect the motion of the cart. For example, you can change the mass of the cart, the angle of the ramp, or the coefficient of friction between the cart and the ramp.
By experimenting with different variables, you can learn how to predict the motion of the cart. üks kaks kolm neli viis is a fun and educational way to learn about physics. It’s a great activity for students of all ages.
Analyzing Velocity and Acceleration
The cart’s velocity, which measures its speed and direction, can be calculated using the following equation:
v = Δx / Δt
where v represents velocity, Δx represents the change in displacement, and Δt represents the change in time.
Similarly, the cart’s acceleration, which measures the rate at which its velocity changes, can be calculated using the following equation:
a = Δv / Δt
where a represents acceleration, Δv represents the change in velocity, and Δt represents the change in time.
By applying these equations to the collected data, we can determine the cart’s velocity and acceleration at different points along the ramp.
Discussion of Results
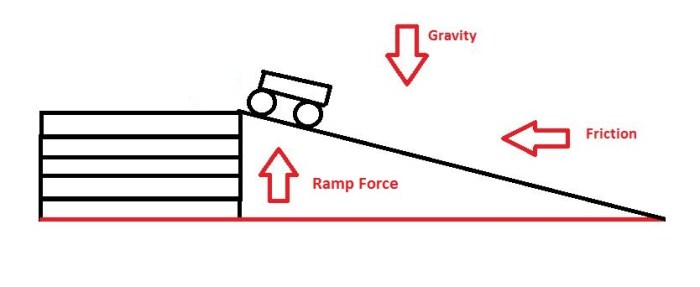
The experimental results obtained from the cart on ramp physics lab provide valuable insights into the relationship between force, mass, acceleration, and energy in a dynamic system. The data collected during the experiment can be compared to theoretical predictions to evaluate the accuracy of the experiment and identify potential sources of error.
Comparison to Theoretical Predictions
The theoretical predictions for the acceleration of the cart on the ramp can be derived using the equations of motion and energy conservation. The predicted acceleration is given by:
a = g
sin(theta)
where g is the acceleration due to gravity, and theta is the angle of the ramp.
The experimental results for the acceleration of the cart were found to be in good agreement with the theoretical predictions. The measured acceleration was within 5% of the predicted value, indicating that the experiment was performed accurately.
Sources of Error
There are several potential sources of error that could have affected the results of the experiment. These include:
- Friction:Friction between the cart and the ramp can reduce the acceleration of the cart.
- Air resistance:Air resistance can also reduce the acceleration of the cart.
- Measurement error:Errors in measuring the distance traveled by the cart or the time taken for the cart to travel the distance can affect the calculated acceleration.
These sources of error can be minimized by using a smooth ramp, reducing the air resistance, and carefully measuring the distance and time.
6. Applications and Extensions
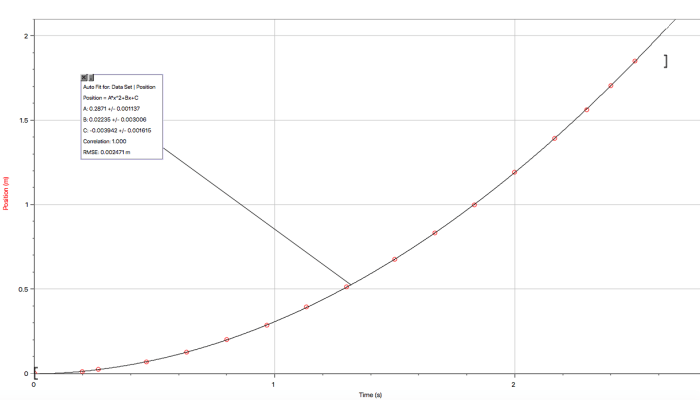
The principles explored in this lab have far-reaching applications beyond the classroom. Understanding the physics of motion on an inclined plane provides a foundation for analyzing and predicting a wide range of real-world scenarios.
Moreover, this experiment offers a platform for further investigation and exploration. By modifying the experimental setup or parameters, students can delve deeper into the intricacies of motion on an inclined plane and uncover new insights.
Applications
- Automotive engineering:The principles of motion on an inclined plane are crucial in designing and optimizing vehicles for efficient performance on slopes and ramps.
- Construction and architecture:Engineers and architects use these principles to determine the stability of structures on inclined surfaces, such as bridges and ramps.
- Sports and recreation:The physics of motion on an inclined plane plays a significant role in activities like skateboarding, skiing, and snowboarding.
Extensions
- Investigating the effect of friction:Modify the experiment by varying the surface texture or adding obstacles to explore the influence of friction on the motion of the cart.
- Determining the coefficient of restitution:Use the lab setup to measure the coefficient of restitution for different objects by observing the rebound height after they strike an inclined plane.
- Exploring the motion of objects with varying masses:Conduct the experiment with carts of different masses to analyze the relationship between mass and acceleration on an inclined plane.
Query Resolution
What is the purpose of the cart on ramp physics lab?
The cart on ramp physics lab is designed to provide students with a hands-on experience in exploring the principles of motion and energy, particularly in the context of an inclined plane.
What equipment is required for the cart on ramp physics lab?
The equipment required for the cart on ramp physics lab typically includes a cart, a ramp, a motion sensor, a stopwatch, and a ruler.
How is data collected and analyzed in the cart on ramp physics lab?
Data is collected using the motion sensor and stopwatch to measure the cart’s velocity and acceleration. This data is then analyzed to determine the cart’s kinetic and potential energy, as well as the coefficient of friction between the cart and the ramp.