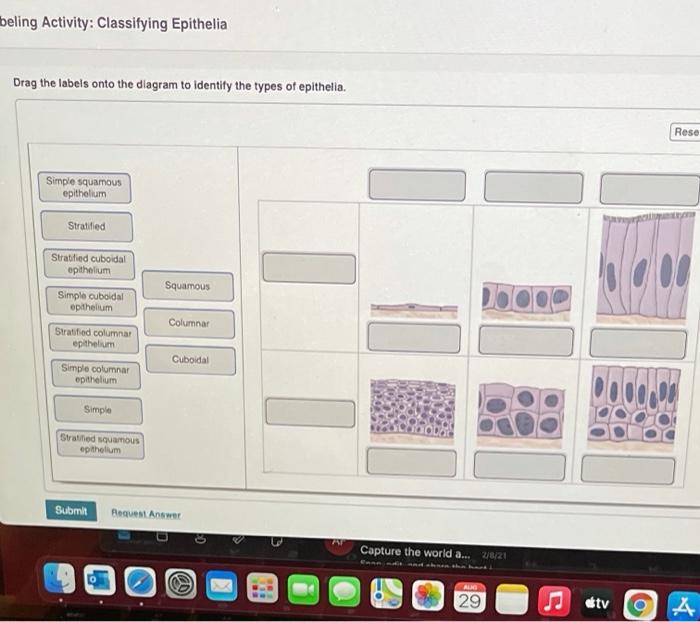
Drag the labels onto the four types of tissue membranes. – In the realm of biology, tissue membranes play a pivotal role in the structure and function of living organisms. Drag the labels onto the four types of tissue membranes to explore the fascinating world of these delicate yet resilient barriers that shape our bodies.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue membranes, unraveling their unique compositions, specialized functions, and diverse applications in medicine and industry.
Tissue Membranes
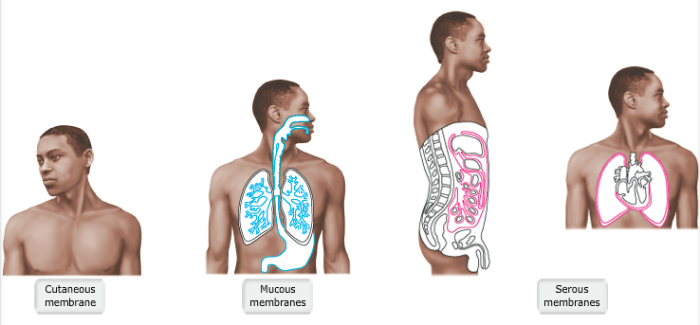
Tissue membranes are thin layers of cells that line the surfaces of the body and its cavities. They protect the body from the environment, regulate the passage of substances into and out of the body, and provide support and cushioning.
Types of Tissue Membranes
- Epithelial membrane
- Connective tissue membrane
- Muscle membrane
- Nervous tissue membrane
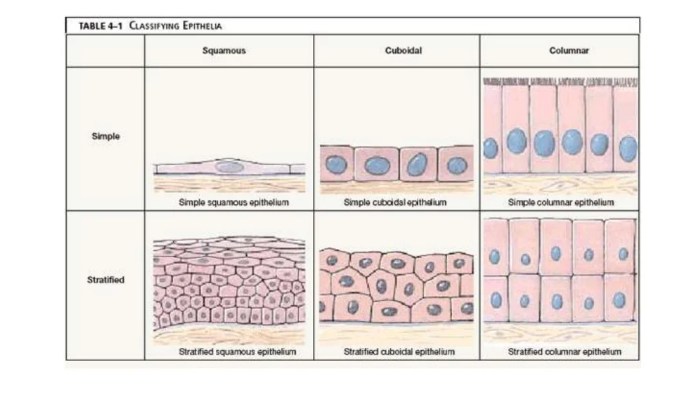
Epithelial Membrane
Epithelial membranes are composed of closely packed cells that line the surfaces of the body and its cavities. They protect the body from the environment, regulate the passage of substances into and out of the body, and provide support and cushioning.
Examples of epithelial membranes include the skin, the lining of the digestive tract, and the lining of the respiratory tract.
Connective Tissue Membrane
Connective tissue membranes are composed of cells that are embedded in a matrix of collagen and other proteins. They provide support and cushioning for the body’s organs and tissues.
Examples of connective tissue membranes include the tendons, ligaments, and fascia.
Muscle Membrane, Drag the labels onto the four types of tissue membranes.
Muscle membranes are composed of muscle cells that are arranged in bundles. They allow the body to move by contracting and relaxing.
Examples of muscle membranes include the muscles of the arms, legs, and back.
Nervous Tissue Membrane
Nervous tissue membranes are composed of neurons and glial cells. They transmit electrical signals throughout the body, allowing the body to communicate and respond to its environment.
Examples of nervous tissue membranes include the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Frequently Asked Questions: Drag The Labels Onto The Four Types Of Tissue Membranes.
What are the key functions of tissue membranes?
Tissue membranes serve as protective barriers, regulate substance exchange, provide structural support, facilitate communication, and contribute to movement.
How do epithelial membranes differ from connective tissue membranes?
Epithelial membranes are composed of tightly packed cells that form a continuous sheet, while connective tissue membranes are characterized by a loose arrangement of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix.
What is the role of muscle membranes in the body?
Muscle membranes surround muscle fibers and facilitate the transmission of electrical impulses that trigger muscle contractions.