In the realm of thermodynamics, the difference between latent heat and sensible heat emerges as a captivating concept, inviting us to unravel the intricacies of heat transfer and its diverse applications. This exploration delves into the defining characteristics, mechanisms, and practical implications of these two distinct forms of heat, shedding light on their significance in various scientific and engineering domains.
Latent heat, characterized by its ability to induce phase changes without altering temperature, stands in contrast to sensible heat, which directly influences temperature variations. This fundamental distinction serves as the cornerstone of this discourse, as we embark on a journey to decipher the nuances of each form and their interplay in shaping the world around us.
Difference between Latent Heat and Sensible Heat
Latent heat and sensible heat are two distinct forms of heat that play important roles in various physical processes and engineering applications. Understanding the difference between these two types of heat is crucial for comprehending heat transfer phenomena.
Definition and Distinction, Difference between latent heat and sensible heat
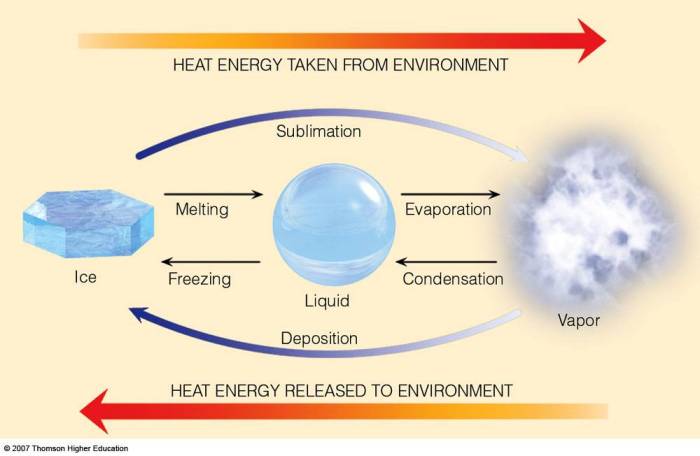
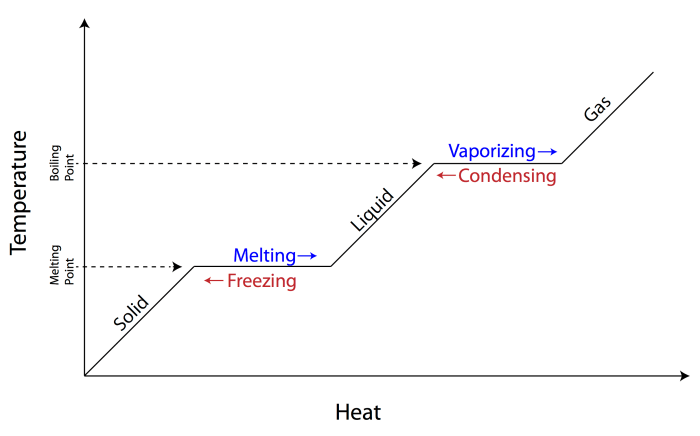
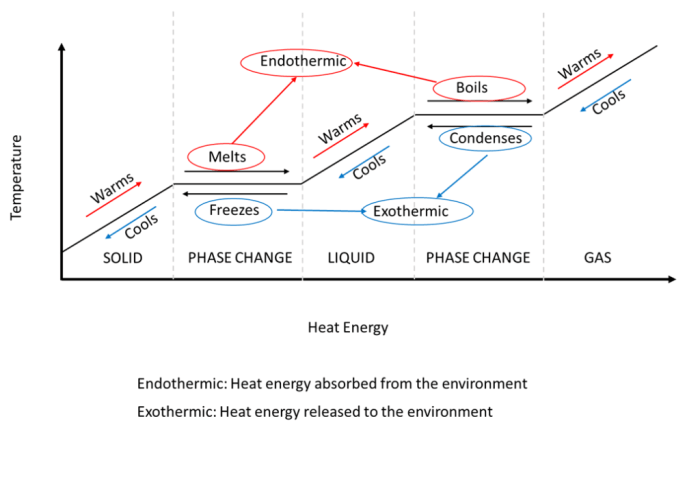
Latent HeatLatent heat is the amount of heat absorbed or released by a substance during a phase change, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, or condensation. It is associated with a change in the physical state of the substance, but not with a change in its temperature.Sensible
HeatSensible heat is the amount of heat that causes a change in the temperature of a substance. It is associated with the increase or decrease in the kinetic energy of the molecules in the substance.Key DifferencesThe key differences between latent heat and sensible heat are:
-
-*Phase Change
Latent heat involves a phase change, while sensible heat does not.
-*Temperature Change
Latent heat does not cause a temperature change, while sensible heat does.
-*Energy Transfer
Latent heat is involved in the transfer of energy between a substance and its surroundings during a phase change, while sensible heat is involved in the transfer of energy within a substance.
Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
Latent Heat TransferLatent heat transfer occurs when a substance undergoes a phase change. For example, when ice melts, it absorbs latent heat from the surroundings. This heat is used to overcome the intermolecular forces holding the water molecules in a solid state, allowing them to become a liquid.Sensible
Heat TransferSensible heat transfer occurs when the temperature of a substance changes. For example, when a pot of water is heated on a stove, it absorbs sensible heat from the flame. This heat causes the water molecules to move faster, increasing their kinetic energy and resulting in a higher temperature.Comparison
of Heat Transfer MechanismsLatent heat transfer is more efficient than sensible heat transfer because it involves a larger amount of energy transfer for a given temperature change. This is because the energy required to overcome intermolecular forces during a phase change is typically much greater than the energy required to increase the kinetic energy of molecules.
Applications and Examples
Latent Heat
-
-*Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
Latent heat is utilized in refrigeration and air conditioning systems to remove heat from a space. The refrigerant undergoes a phase change from liquid to gas, absorbing latent heat from the surroundings.
-*Thermal Energy Storage
Latent heat storage systems use materials that can absorb and release large amounts of latent heat. These systems are used to store thermal energy for later use, such as in solar heating systems.
Sensible Heat
-
-*Heating Systems
Sensible heat is used in heating systems to raise the temperature of a space. Heaters, such as furnaces and radiators, transfer sensible heat to the air, which then circulates throughout the space.
-*Cooking
Sensible heat is applied in cooking to increase the temperature of food. Ovens, stoves, and microwaves all use sensible heat to cook food.
Practical ImplicationsUnderstanding the difference between latent and sensible heat has practical implications in various fields:
-
-*Energy Efficiency
Engineers can design more energy-efficient systems by optimizing the use of latent and sensible heat.
-*Thermal Comfort
Latent heat can be used to improve thermal comfort in buildings by controlling humidity levels.
-*Industrial Processes
Latent heat is used in industrial processes such as metalworking, where it is necessary to melt or solidify materials.
Measurement and Calculations
Latent Heat MeasurementLatent heat is typically expressed in units of energy per mass, such as joules per kilogram (J/kg). It can be measured using calorimetry, where the amount of heat absorbed or released during a phase change is determined.Sensible Heat CalculationSensible heat transfer can be calculated using the formula:“`Q = mcΔt“`where:
- Q is the amount of sensible heat transferred (in joules)
- m is the mass of the substance (in kilograms)
- c is the specific heat capacity of the substance (in J/(kg·K))
- Δt is the change in temperature (in Kelvin)
Formulas for Latent HeatThe latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat required to melt a solid at its melting point. It is expressed as:“`L_f = mΔH_f“`where:
- L_f is the latent heat of fusion (in joules)
- m is the mass of the substance (in kilograms)
- ΔH_f is the specific latent heat of fusion (in J/kg)
The latent heat of vaporization is the amount of heat required to vaporize a liquid at its boiling point. It is expressed as:“`L_v = mΔH_v“`where:
- L_v is the latent heat of vaporization (in joules)
- m is the mass of the substance (in kilograms)
- ΔH_v is the specific latent heat of vaporization (in J/kg)
Detailed FAQs
What is the primary difference between latent heat and sensible heat?
Latent heat involves energy transfer during phase changes without temperature change, while sensible heat directly influences temperature variations.
How is latent heat utilized in practical applications?
Latent heat finds applications in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, where it facilitates cooling processes by absorbing heat during phase transitions.
What are some examples of sensible heat applications?
Sensible heat is employed in heating systems and cooking appliances, where it raises the temperature of objects or substances.