Embark on a journey of discovery with “odw 5e ch03 label the motherboard,” an in-depth exploration of the vital component that orchestrates the symphony of computer hardware. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the intricacies of motherboards, empowering you with a profound understanding of their functions, components, and features.
Unveiling the secrets of the motherboard, we will delve into its purpose, examining its role as the central hub connecting all essential computer elements. We will dissect its layout, identifying key components such as the CPU socket, memory slots, expansion slots, storage connectors, and power connectors.
Moreover, we will explore the diverse motherboard form factors, contrasting their advantages and disadvantages.
Motherboard Overview
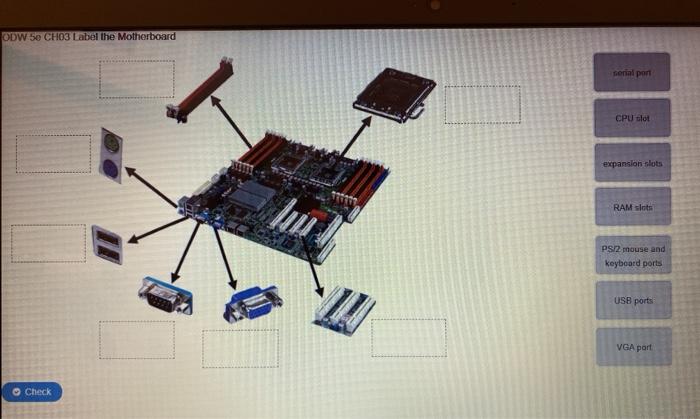
A motherboard is the central component of a computer system, connecting all the other components and allowing them to communicate with each other. It provides the physical structure and electrical connections for the CPU, memory, storage, expansion cards, and other devices.
Motherboards come in various form factors, each with its own set of features and capabilities. The most common form factor is ATX, which is used in most desktop computers. Other form factors include micro ATX, mini ITX, and extended ATX (EATX), which are designed for smaller or larger systems.
Motherboard Components
The key components of a motherboard include:
- CPU socket: The socket where the CPU is installed.
- Memory slots: The slots where the memory modules are installed.
- Expansion slots: The slots where expansion cards, such as graphics cards and sound cards, are installed.
- Storage connectors: The connectors where storage devices, such as hard drives and SSDs, are connected.
- Power connectors: The connectors where the power supply is connected.
Motherboard Form Factors: Odw 5e Ch03 Label The Motherboard
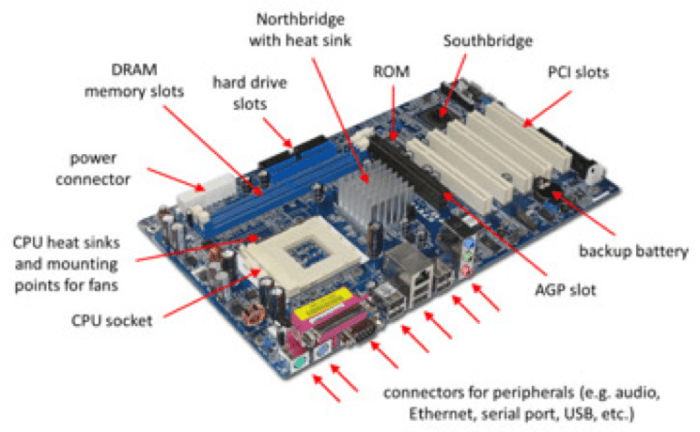
Motherboard form factors are standardized sizes and shapes that define the physical dimensions and layout of the motherboard. The most common form factors are ATX, micro ATX, and mini ITX.
ATX is the most common form factor for desktop computers. It is a full-sized motherboard that provides plenty of space for expansion cards and other components.
Micro ATX is a smaller form factor than ATX. It is designed for smaller systems, such as home theater PCs and gaming consoles.
Mini ITX is the smallest form factor. It is designed for very small systems, such as embedded computers and industrial PCs.
Motherboard Features
Motherboards come with a variety of features, including:
- BIOS settings: The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a firmware that is stored on the motherboard. It provides the basic instructions for the computer to boot up and operate.
- Overclocking capabilities: Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed of the CPU or other components. Some motherboards have built-in overclocking features that allow users to overclock their systems.
- Integrated graphics: Some motherboards have integrated graphics, which is a graphics processor that is built into the motherboard. This allows users to use their computers without having to install a separate graphics card.
- Wireless connectivity: Some motherboards have built-in wireless connectivity, which allows users to connect their computers to Wi-Fi networks.
Motherboard Troubleshooting
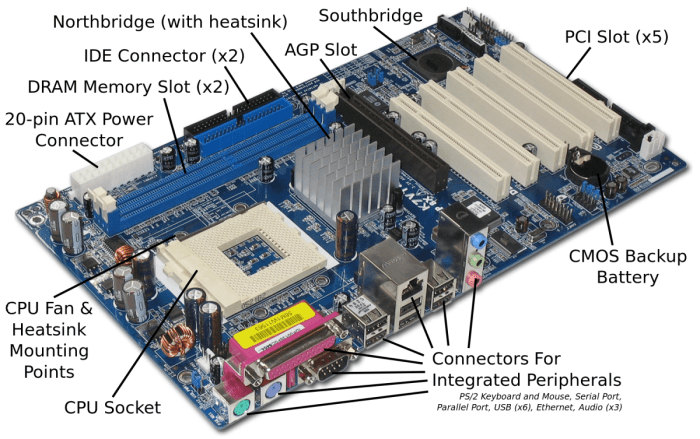
Motherboard problems can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Faulty components
- Overheating
- Power supply issues
- BIOS corruption
To troubleshoot motherboard problems, it is important to first identify the symptoms. These symptoms can include:
- The computer will not boot up.
- The computer is unstable and crashes frequently.
- The computer is overheating.
- The computer is making strange noises.
Advanced Motherboard Concepts
Advanced motherboard concepts include:
- Virtualization support: Virtualization is a technology that allows multiple operating systems to run on a single physical computer.
- RAID configurations: RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology that combines multiple storage devices into a single logical unit.
- Multi-GPU setups: Multi-GPU setups are used to improve graphics performance by using multiple graphics cards in a single computer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of a motherboard?
The motherboard serves as the central hub, connecting all vital computer components and facilitating communication between them.
What are the key components of a motherboard?
Key components include the CPU socket, memory slots, expansion slots, storage connectors, and power connectors.
What are the different motherboard form factors?
Common motherboard form factors include ATX, micro ATX, and mini ITX, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.